Hi Legends!!👋 In this article we're gonna learn about IPv4 Addressing!
Let's start: 😉
What is an IP Address?
An IP address is a unique address that identifies a device on the internet or a local network. IP stands for "Internet Protocol," which is the set of rules governing the format of data sent via the internet or local network.
When you go online for email, to shop or chat, your request has to be sent out to the right destination, and the responses you want need to come back directly to you. An IP address plays a significant role in that.
To make sure you can do your thing on the Internet, your computer’s networking software is hardwired to follow a list of built-in networking standards and rules to connect to Internet.
One of those networking protocols on your computer, the Internet Protocol, is responsible for addressing, delivering and routing your online requests precisely.The address it uses is the IP address for your connection.
An IP address is a string of numbers separated by periods. IP addresses are expressed as a set of four numbers — an example address might be 192.158.1.38. Each number in the set can range from 0 to 255. So, the full IP addressing range goes from 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255.
IP address works like a house number or a phone number which is what you need as a contact…that’s the mindset!
Currently there are 2 versions of IP addresses are in use i.e
- IPV4
- IPV6
IP Addresses are of 4 Types i.e
- Public
- Private
- Fixed
- Dynamic
So legends, 😎 I am sure that you all are totally clear by the concept!! Let's dive into our main concept :
What is the IPv4 Address ?
IPv4 addresses are 32-bit integers that can be expressed in hexadecimal notation. The more common format, known as dotted quad or dotted decimal, is x.x.x.x, where each x can be any value between 0 and 255. For example, 192.0.2.146 is a valid IPv4 address.
It is divided into 4 octets(1 octet = 8 bits). They are usually represented in dotted decimals, but binary representation is another way to represent them.
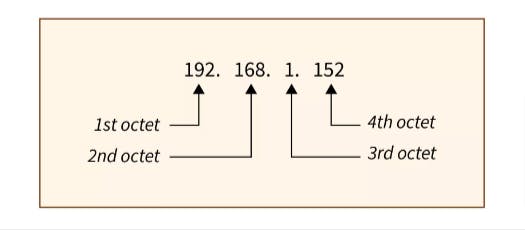
IP Addresses consist of two parts. The first part is network part and the second part is host part. This is determined according to Subnet Mask.
Subnet Mask is also a number series like IP address, that shows the network portion of an IP address. Subnet Masks are used together with IP addresses. Subnet Mask can be like 255.255.255.0. As binary, this is 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000. Here, 1’s are representing the network side. 0’s are representing host side.
Let’s show this with the IP address 192.168.2.1. For example we will use the Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0. This subnet mask’s binary written is like 11111111.11111111.11111111.00000000 . It is saying that, the first 3 octet (first 24 bits) shows the network part. Because it is full of 1s. The last octet is full of 0s and it shows hosts. 1s are for network and 0s are for host devices in this network. So, in the last case, we can say that all the devices in this network will use the same network part (192.168.2).
But host part can change from 0 to 255 like below:
- 192.168.2.0
- 192.168.2.1
- 192.168.2.2
- 192.168.2.3
- ......
- 198.2.255
Here;
- The first address 192.168.2.0 is the network address.
- The last address 192.168.2.255 is the broadcast address.
- The other addresses from 192.168.2.1 to 192.168.2.254 can be used for a device in the same network.
What is Classful Addressing?
Classful addressing is a technique of allocating IP addresses that divides them into five categories.
For different sized networks, different IP Address Class is used.These IP Address Classes has strict borders.
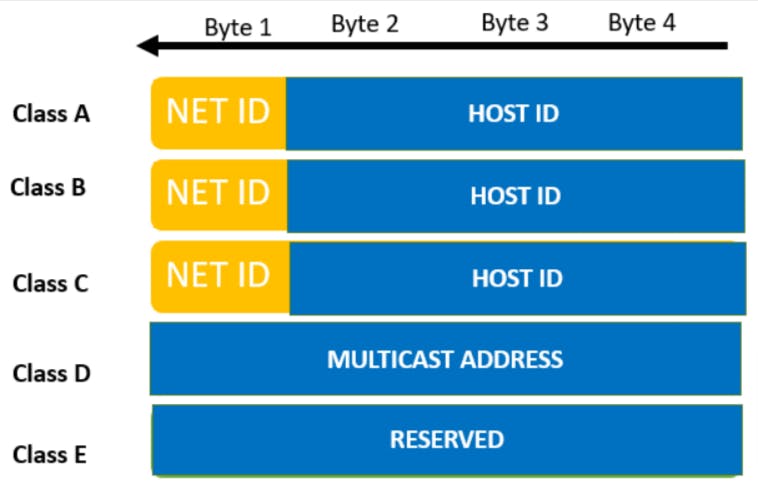
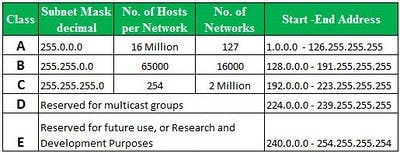
The 32 bit IP address is divided into five sub-classes. These are:
- Class A (1.0.0.0 to 126.255.255.255)
- Class B (128.0.0.0 to 191.255.255.255)
- Class C (192.0.0.0 to 223.255.255.255)
- Class D (224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255)
- Class E (240.0.0.0 to 254.255.255.255)
Network part : The network part is also known as net id which is used to classify the network to which the host is connected.
Host part : The host part is also known as the host id which is the part of the IP address which is used to uniquely identify the host on a network.
Here, 0.0.0.0, 127.0.0.0 and 255.255.255.255 addresses are reserved for various roles. These reserved address roles are:
- 0.0.0.0 – Used for Default Routes
- 127.0.0.0 – Used for Loopback
- 255.255.255.255 – Used for Broadcast
IPv4 Addressing Modes
Sending data over the Internet can happen in several ways. IPv4 supports three of these addressing modes, which are:
Unicast addressing mode: In this mode, the data gets sent to only one host. The destination address field contains only the IPv4 address of the destination host. A computer sends data to a target server. It is a one-to-one transmission. It is what happens when a user sends an email to a single recipient.
Broadcast addressing mode: In this data is sent to all the devices in the network, i.e., multiple hosts. The destination address field of the packet consists of the IP address called the Special Broadcast address which is represented by 255.255.255.255255.255.255.255. It is how mass mailers get sent to all connected recipients.
Multicast addressing mode: This is a combination of the unicast and broadcast addressing modes. It can be one-to-many or many-to-many transmission. In this mode, the destination address includes a unique address that begins with 224.x.x.x, which can be accommodated by more than one host. Like marketing campaigns would use multicast addressing mode to only reach desired audiences (for example, a specific country).
Super guys🥳🎉, we have cracked the concept of IPv4 !! Let's learn some limitation of it:
What Are the Limitations of IPv4?
- The lack of address space - the number of different devices connected to the Internet grows exponentially, and the size of the address space is quickly depleted;
- Since the Internet was created in the USA, this country is also involved in the distribution of IP addresses. Almost 50% of all addresses are reserved for the United States.
- No means are provided to limit access to information hosted on the network. IPv4 has never been designed for security.
Thank you for giving my blog a read. Hope it helped you and you learned something new.😊❤️❤️
Please feel free to reach out if you have any thoughts or feedback, I'm always happy to get constructive feedback and to keep learning!💙

